VLAN Explained in Networking
Have you ever wondered how large companies keep their networks clean, secure, and organized, especially when hundreds of devices are connected? VLANs are the answer. This guide will explain VLANs in networking using simple language. This article is for anyone who wants to learn more about VLANs, whether they are new to networking or just brushing up on their IT skills. It will explain the basics and how they work. You’ll also find out what types of VLANs there are, as well as the benefits.
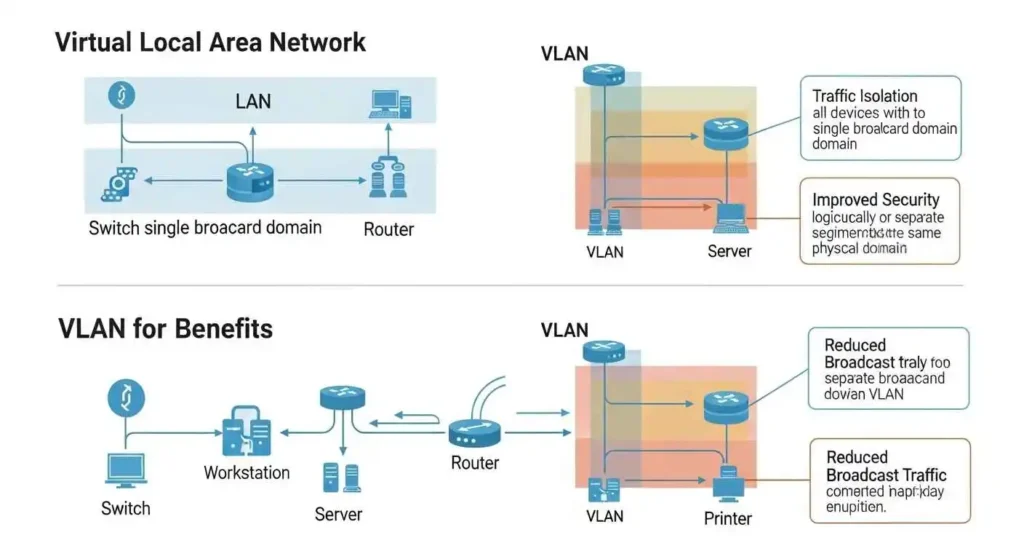
Imagine an office that has Sales, HR and IT teams. All their devices would be on the same network, creating noise, clutter and security risks. With VLANs, each department has its own private hall–even if they are in the same building.
What is VLAN, and why is it used?
VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network. It is a method to create different virtual networks using the same switch or infrastructure. Devices within the same VLAN are able to communicate, but those in other VLANs can’t unless they have routing enabled.
Why Use VLANs
-
Increase security with the isolation of sensitive data
-
To reduce network traffic
-
To improve performance
-
To simplify network management
This is particularly useful in environments where departments or functions must be separated, for both safety and efficiency.
Types of VLAN—Know the Differences
Understanding the different types of VLANs will help you select the best one for your network. The VLAN types are listed below.
Static VLAN (Port-Based VLAN)
Each port of the switch is assigned a VLAN. This is like assigning seats in a class: who sits where, and when, is fixed.
Protocol-Based VLAN
Traffic is classified based on the network protocol, such as IPX or AppleTalk.
VLAN MAC Address Based
The MAC address is used to group devices. It acts as a digital fingerprint.
Policy-Based VLAN
You can assign VLANs dynamically using rules such as user roles, applications, or even the time of day.
Voice VLAN
A special VLAN is created for VoIP devices (Voice Over IP), such as IP phones, to ensure low latency and clear audio.
VLAN vs. LAN—What’s the Difference?
The traditional Local Area Network (LAN) connects the devices at the same physical location. All devices are in the same broadcast domain.
A VLAN will allow these devices to be virtually separated even if they are physically connected to the switch. This reduces the broadcast traffic and increases security.
| Features | LAN | VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Physical | Logical/Virtual |
| Flexibility | Low-cost | High-quality |
| Scalability | Limited | Easy to scale |
| The Security of Your Own Home | Basic | Advanced isolation and Control |
VLAN Configuration—Step-by-Step Setup Guide
It’s not difficult to set up a configuration. Here is a 7-step guide that simplifies the process:
Step 1: Determine VLAN requirements
Separate departments or functions (e.g., sales, HR, and IT).
Step 2: Access your switch/router.
Log in to the switch with administrator credentials.
Step 3: Create VLANs
Create VLANs using the GUI or commands (e.g. vlan10).
Step 4: Assign ports to VLANs
Identify which ports belong to each VLAN.
Step 5: Configure Trunk Ports
Use VLAN tagging to create trunk links that allow for multiple VLANs over a single cable.
Step 6: Enable Inter-VLAN Routing
Use a layer 3 switch or router to allow communication between VLANs.
Step 7: Test the Monitor
Use tools such as ping or monitoring software to check connectivity and isolation of VLANs.
VLAN Ex: Segmentation within a Company
Imagine a business with three departments.
-
Sales (VLAN 10)
-
Marketing (VLAN 20).
-
IT (VLAN 30).
Switch ports are assigned to each department.
-
Ports 1-10: Sales
-
Ports 11-20: Marketing
-
Ports 21-30
This will ensure that:
-
Sales data stays private
-
The IT system is not overloaded by marketing traffic
-
Access between departments is strictly controlled
InterVLAN routing allows for certain communication between departments.
What is VLAN?
When a device transmits data over a VLAN
-
The switch adds a VLAN tag to the data frame.
-
If it is going to another switch, the tagged frame will be sent via trunk links.
-
The switch that receives the frame reads the tag and only sends it to the ports of the same VLAN.
-
The tag is removed when it reaches its destination.
This system of tagging allows for multiple VLANs on the same cable to remain isolated.
FAQs: All of Your VLAN Enquiries Are Addressed
Why is VLAN utilized, and what is it?
Even if devices are on the same physical network, they can be conceptually divided into groups using a virtual local area network, or VLAN. It is employed to ease management, lessen network congestion, and improve security.
Can you explain VLAN to GeeksforGeeks?
A logical division of a LAN that puts devices together and isolates their traffic from other groups is known as a VLAN, according to GeeksforGeeks.
How does VLAN operate, and what is it?
Traffic is given a distinct VLAN ID by a VLAN. This ID is used by switches to make sure that only devices in the same VLAN can speak to each other directly. Trunk ports and VLAN tags aid in maintaining traffic organization across switches.
VLAN illustration?
To protect sensitive systems from visitor traffic, Company “X” divides HR (VLAN 10), IT (VLAN 20), and guest Wi-Fi (VLAN 30).
How is the VLAN configured?
Creating VLAN IDs, allocating switch ports, turning on trunk ports, and configuring routing are all part of VLAN configuration.
VLAN Types?
Port-Based
Tag-Oriented
Voice VLAN
VLAN for management
Based on Protocols
MAC-Based
In network architecture, each fulfills a distinct purpose.
LAN versus VLAN?
A VLAN is virtual, whereas a LAN is physical. More control, flexibility, and scalability are provided by VLANs, particularly in contemporary network systems.
What is the full form of VLAN?
Virtual Local Area Network is what VLAN stands for.
Are VLANs Ready for Use? Selecting the Appropriate Network Management Tool
Don’t simply learn about VLANs if you want to set them up in your workplace or company; use reliable solutions like NinjaOne RMM to easily monitor and manage them.
It enables you to:
Keep an eye on devices linked to VLANs.
Segment networks automatically.
Ensure secure and easy communication.
Take charge of your network like a pro by starting your free NinjaOne trial now!
Concluding Remarks
Describe how networking VLANs don’t have to be scary. Consider VLANs as virtual partitions that keep a single area neat, safe, and effective. Understanding and putting into practice VLANs can significantly enhance the health of your network, regardless of your level of expertise.